Object Details
Culture
Valdivia (Ecuador)
Date
ca. 1400 BCE
Medium
Carved stone
Dimensions
Overall: 8 3/4 × 4 3/4 × 3/4 inches (22.2 × 12 × 1.9 cm)
Credit Line
Gift of Emile Deletaille and Lin Crocker-Deletaille
Object
Number
94.020
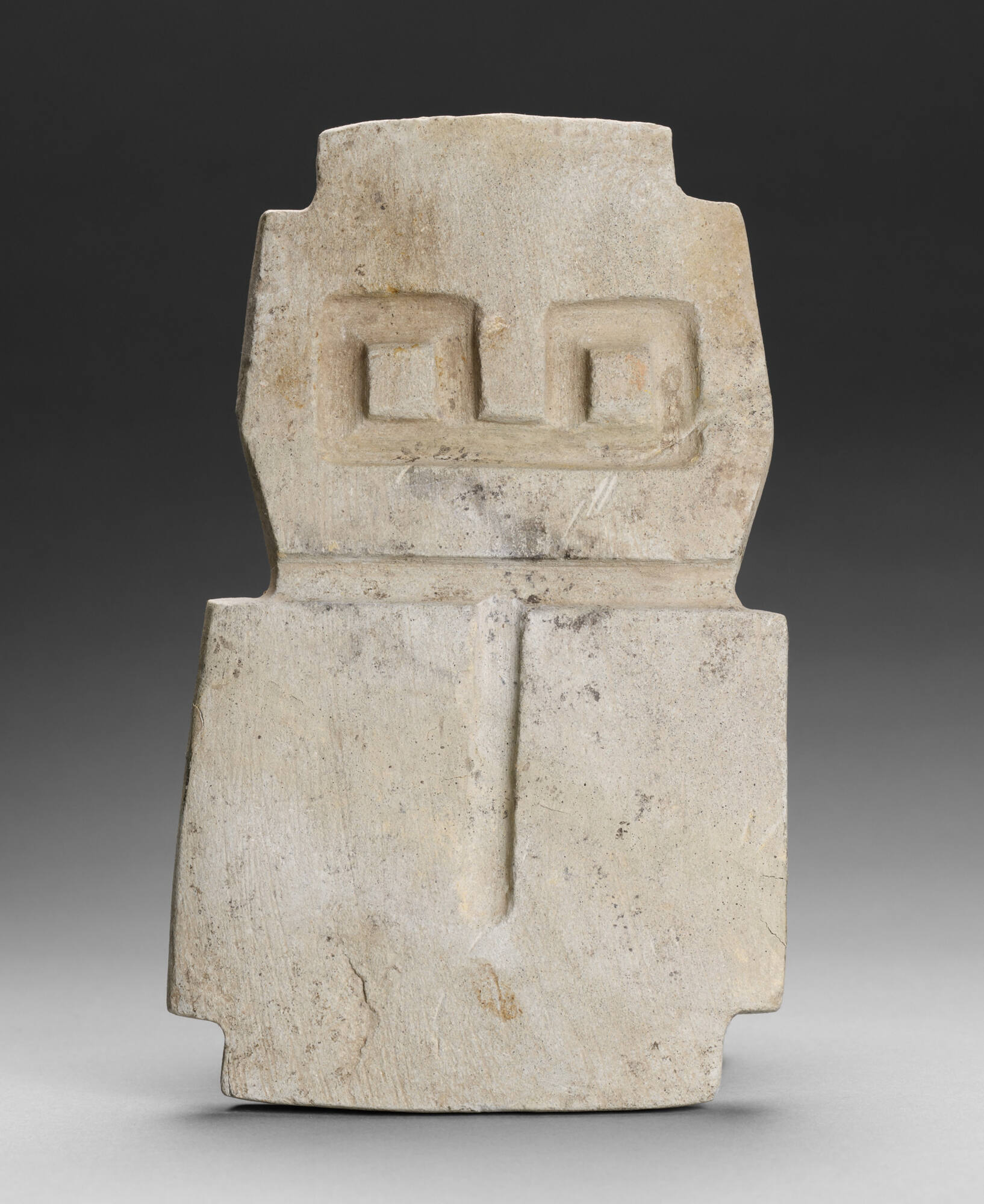
BRIEF DESCRIPTIONThis carved stone sculpture is of an anthropomorphic figure.WHERE WAS IT MADE?This (…)
BRIEF DESCRIPTIONThis carved stone sculpture is of an anthropomorphic figure.WHERE WAS IT MADE?This sculpture was made in what is now Ecuador.HOW WAS IT MADE?Hand tools made from harder stones, as well as sinew or fiber cords, were used to shape the stone. To ease the work, sand was used as an abrasive, and water as a lubricant.HOW WAS IT USED?The original function of archaeological figurines found in museum collections is uncertain. Today archeologists carefully record information about the associations between artifacts and the circumstances of their burial as they are unearthed, and we can draw many conclusions about object function. However, very few of the archaeological objects found in museums today were excavated in a careful, scientific manner, so we have fewer clues about their past associations and function.WHY DOES IT LOOK LIKE THIS?This figure has large round eyes, and may represent a human or an animal. Aspects of many different animals can be found on pre-Columbian pottery, textiles, and metalwork. They depict wild and domesticated animals, creatures commonly encountered in everyday life, and creatures found rarely–or not at all–in the natural world. These animals are often mixed with human attributes in what may appear to us to be startling fantasy combinations.ABOUT THE VALDIVIA CULTURE:The Valdivia culture was centered on the arid Santa Elena Peninsula. Although primarily regarded as a coastal culture, Valdivia influence also extended inland, where many of its agricultural settlements were located. Valdivia is famous as one of the earliest pottery-producing cultures in South America, and is noted for its “Venus” figurines, most of which depict stylized women with rudimentary features. One of the original “cradles of civilization” in South America, innovations in pottery technology spread outward from Valdivia to other cultural groups and eventually gave rise to the rich ceramic traditions of the later high civilizations. Such quintessentially Andean traits as the use of coca leaves and the practice of weaving cotton textiles (and perhaps using shellfish-derived purple dyes to color them) were already present at Valdivia. The population lived in tribal chiefdoms comprised of lineage groups, in settlements that included dedicated ritual areas as well as residential spaces. While the origins of the Valdivia people are unclear, they appear to have had a relationship with the tropical forests of lowland Amazonia, perhaps by descent or through trade. The Valdivia culture gave rise to the subsequent Machalilla culture.